Build a Repeatable Revgen System For Your Digital Agency
How digital agencies can design and implement repeatable revenue generation systems to achieve sustainable growth.
Executive Summary
Digital agencies rely on four core functions to generate revenue. Business development, Marketing, Sales, and Account Management. All revenue-generating activities will fall under the purview of someone acting in one of those functions. This guide will explore what those roles do, how they’re structured, and how they evolve as agencies grow.
The typical agency will spend 7.1% of its revenue on revgen activities. This has been good enough to deliver an average annual growth rate of 13% since 2015, far below most agency leader’s aspirations. As shops grow, their structure and roles evolve. Smaller shops rely more heavily on owners to generate revenue, while larger agencies distribute the revgen load across many roles and departments.
The way revgen at digital agencies is handled today is fundamentally broken. The current setup results in a feast-or-famine cycle of sales, poor alignment, adversarial relationships, and continually undifferentiated value propositions. This is reflected in the wide variety of growth rates between those agencies that have dialed in their revgen systems, and the slower-growing ones that haven’t.
A better way to run revgen at digital agencies is to fully integrate the four core functions of Bizdev, Marketing, Sales, and Account Management. This requires restructuring revgen activities, elevating account management, achieving marketing-sales parity, facilitating new lines of support, and remastering the metrics used to measure success.
The rapid advance of technology is underpinning much of the growth in this industry. From unlocking new growth for marketing teams to facilitating new capabilities for tech, digital agencies at the forefront of their industry are in an incredible position. By mastering their revgen system, they’ll be able to capitalize on this potential and grow at sustainably higher rates.
About the Author
Nicholas Petroski is the founder of Promethean Research.
Since 2015, he has helped over 100 digital agency owners better understand their industry and chart more effective paths to success.
Prior to cofounding Promethean, Nick worked as an equity analyst at a Wall Street firm where he covered the enterprise software and semiconductor industries.
When he’s not in the office, you can find him backpacking around the Midwest or making elaborate firewood in his woodshop.
Contributing Subject Matter Experts
In addition to our survey and interview work, we invited Cathy Atkins and Katie Jennings to contribute their extensive knowledge and experience to this guide.
Cathy is the founder of Metis Communications, a strategic communications and PR firm that’s been instrumental in growing digital agencies and SaaS firms alike.
Katie founded Upwell Consulting after helping grow numerous digital agencies internally as their Director or VP of business development.
Both of these professionals have deep experience guiding digital agencies toward growth, and they were kind enough to lend their expertise to this guide.
The Importance of Repeatable Revgen Systems
Repeatable revenue generation is a systematic and sustainable approach to driving revenue growth that can be replicated over time, without substantial incremental effort or cost. In essence, it’s about creating a business model and operational strategies that reliably convert resources—be it time, labor, or capital—into revenue.
This concept transcends a singular transaction or one-off project completion. It’s about constructing a core operating model and processes where each piece—marketing, sales, business development, and account management—works in sync to consistently attract, win, and retain profitable clients. Repeatable revenue models often involve predictable revenue streams, such as recurring service contracts, retainers, or subscriptions, but can also include successful strategies for consistently winning project-based work.
A Structured Repeatable Revgen System Unlocks:
Smoother, more predictable revenue growth
A key result of implementing a revgen framework is a steady pipeline and improved conversion rates at each stage. This removes leadgen and revgen as barriers to growth. As a result, organizations experience smoother and more predictable revenue growth, allowing for better planning and decision-making.
Profit margin stability and expansion
With the adoption of a revgen framework, capacity fluctuations diminish, enabling utilization rates to stabilize at consistently higher levels. Consequently, organizations enjoy increased and more reliable profit margins.
Improved team morale and retention rates
Predictable revenue generation leads to improved capacity management, reducing both the intensity of peak work periods and idle times. This approach alleviates two significant stressors in an agency environment, promoting greater stability and contributing to overall team satisfaction and motivation.
Secondly, as the agency grows, it provides more professional opportunities for your team and improves retention rates.
The Four Core Revenue Generating Functions at Digital Agencies
There are four main functional areas that generate revenue for companies: business development, marketing, sales, and account management. What follows are descriptions of each and a brief discussion of how they interact with one another.
Business Development
Business development is the creation and management of strategic relationships. It’s tasked with creating partnerships with other organizations that open new opportunities for your firm. This can range from filling gaps in your service offerings (e.g., white labeling) to partnerships that expand your audience or even joint ventures that affect your positioning.
Note that business development isn’t particularly concerned with converting leads to clients. That falls under the Sales role.
Business development is typically the most fragile form of revgen for digital agencies because of how long it takes and how unreliable it is to develop and capitalize on partnerships.
Marketing
Marketing is communication. Your marketing department’s role is to communicate the value your firm delivers. Marketing communicates with everyone: clients, prospects, leads, internal teams, target markets, prospective employees, and potential partners. Their core function is to attract prospects, warm up leads, and make it easier for sales to close the right accounts. Their secondary functions entail facilitating effective communication with potential hires, employees, partners, and vendors, depending on the agency’s specific strategy.
To do this effectively, marketing is tasked with understanding your customer’s and competitors’ goals, challenges, and industry trends. They then distill these findings into positioning, go-to-market, competitive analysis, and other components of a marketing strategy. Finally, the operational side of marketing implements that strategy and course corrects as needed.
Marketing generates revenue more directly than business development but less so than sales or account management. Effective marketing teams will work together with the other revgen functions to act as a force multiplier for them. Strong marketing teams understand that every single touch point a person engages with for a brand is marketing. Customer service, product onboarding, partner engagement, etc., all are marketing.
Sales
The most basic job of your sales department is to convert leads to clients. While marketing is typically tasked with the top of the marketing funnel, sales is responsible for the bottom of the marketing funnel. In addition to that, sales is also responsible for another funnel: the sales funnel. At successful shops, sales is responsible for sourcing and driving their own leads in addition to the ones marketing brings in.
Sales is directly responsible for generating revenue at digital shops.
The sales role at many digital agencies is often handled by someone with a “Business Development” title. “Business development” is often used interchangeably with “sales” but this is incredibly limiting to what business development can accomplish. Through speaking with hundreds of digital shops, we believe this is a result of a serious fear of the word “sales.” Among owners, “sales” seems to conjure up a picture of a used car salesman or a call center full of direct dialers spamming everyone in the phone book. This causes many owners to want to implement “business development” programs where they build real relationships, where they do good work at fair prices, and where they have their client’s best interests at heart. The thing is, that’s exactly what a properly-run sales function does.
Account Management
An account manager at a digital agency serves as a critical liaison between clients and the agency’s internal teams, ensuring seamless communication and effective project execution. They are responsible for understanding client needs, translating them into creative briefs, and collaborating with various departments, such as design, development, and marketing, to deliver successful campaigns. Additionally, account managers proactively identify opportunities for growth and foster long-term relationships by providing exceptional service, expert guidance, and strategic insights tailored to each client’s unique business objectives. Their ultimate goals are to drive client satisfaction, nurture trust, and achieve measurable results that align with client expectations, thus contributing to the agency’s overall success. They typically live under the sales function at most digital agencies. Note that they differ from project managers mainly in their focus on managing the client relationship vs. the specific value delivery process.
Like sales, account management is directly responsible for generating revenue, but unlike sales, it’s only a portion of their focus.
The Typical Digital Agency
What follows is a detailed view of what an average digital agency looks like. From how quickly they grow, how much they charge per hour, how they structure their revgen teams, how much they invest in revgen activities, and the methods they use to price their services.
Revenue Growth
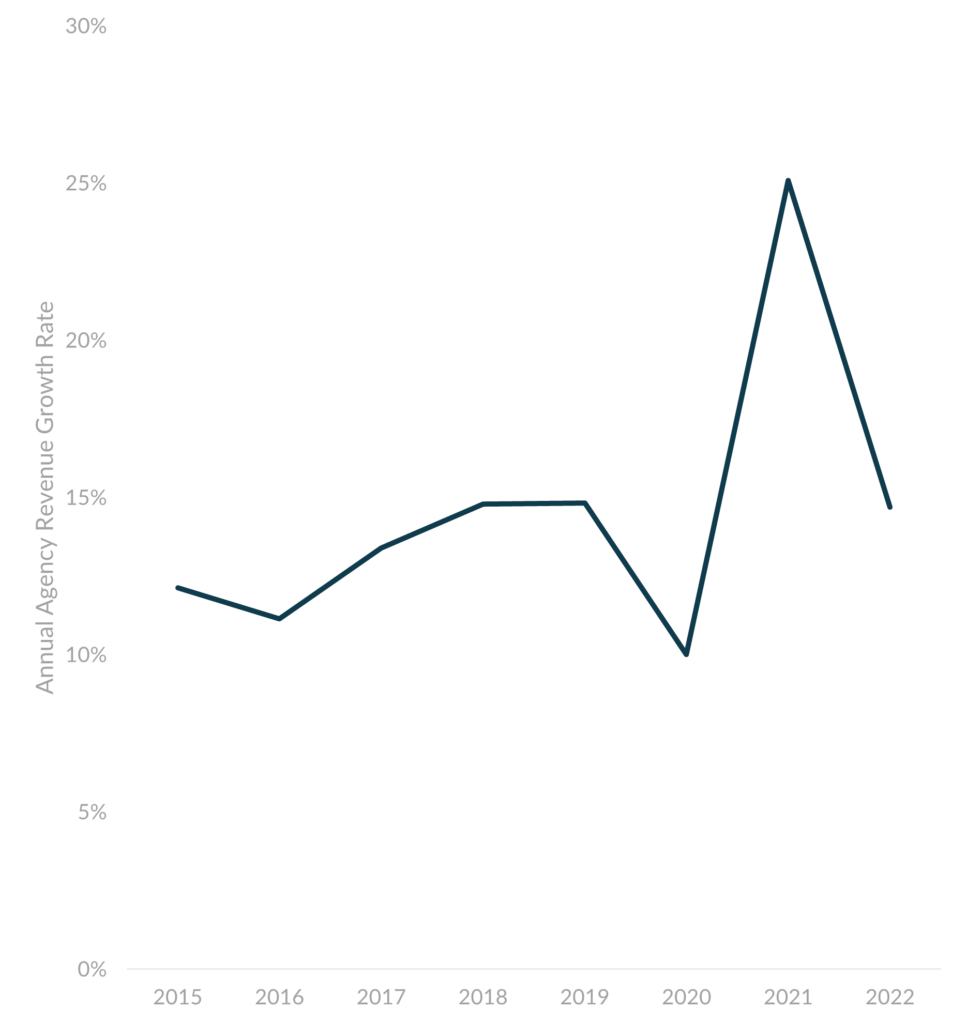
From 2015 to 2020, the average growth rate of agencies in our surveys was 13%. In 2021, the average growth rate almost doubled to 25% due to the enormous demand for digital solutions by corporations. During 2022, we saw revenue growth slow back down to 15%, which is much more in line with historical trends. Check out our latest Digital Agency Industry Report for an updated look at how fast digital agencies grow.
As far as how an agency’s size correlates with growth rates, we see fairly similar rates between Studio (<10 FTE), Small (10-24 FTE), and Medium (25-49 FTE) sized shops. They all tend to grow around 15% a year. This changes when we look at Large (>=50 FTE) shops. They tend to grow 36% faster than the smaller shops.
How Much Digital Agencies Charge Per Hour
What agencies charge plays a major factor in their ability to generate revenue and grow. It’s easy to pick up a large number of clients by under-charging, and it’ll improve closing rates, but it’s a difficult way to grow sustainably. While it’ll improve revgen to a point, it’ll wreak havoc on your margins and increase the fragility of your agency.
Conversely, over-charging will weigh on closing rates and leave you open to significant unused capacity challenges. The additional gain on contracts that do close doesn’t always make up for this, especially during an economic downturn. This is why pricing appropriately is critical to sustainable revgen.
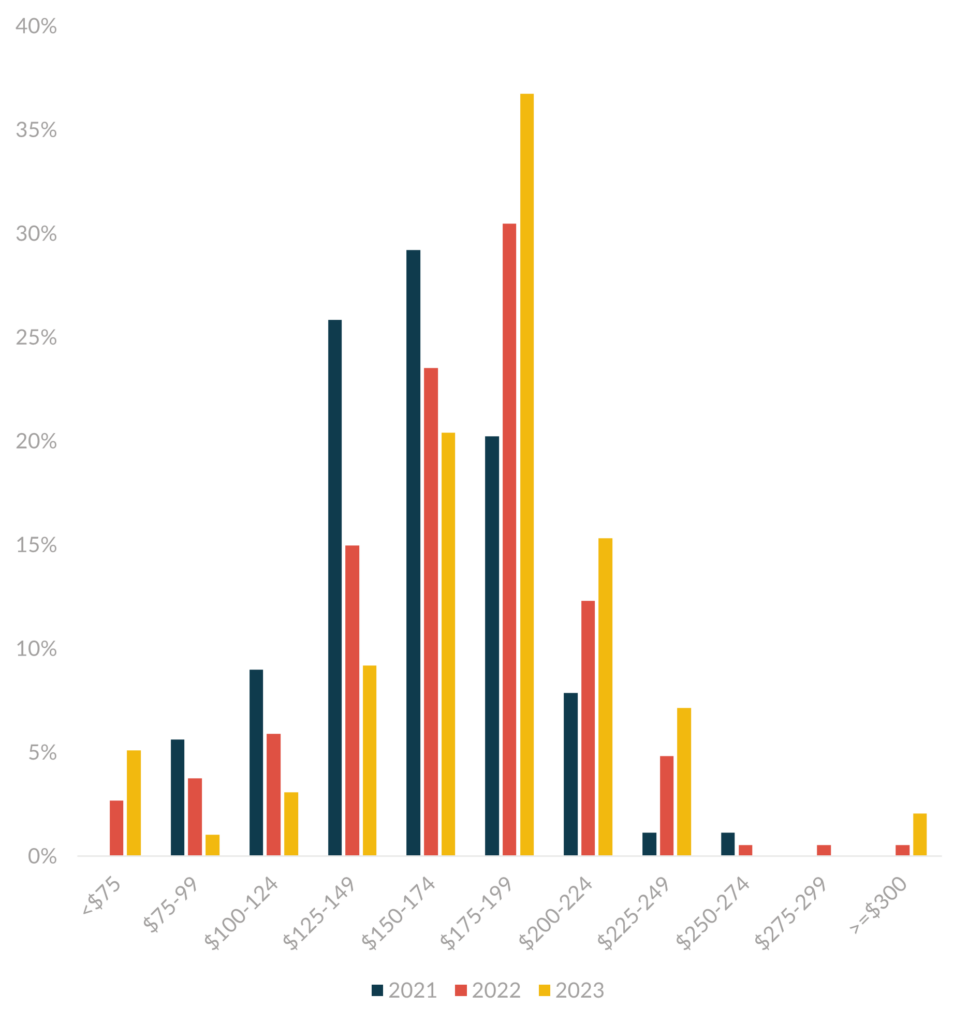
38% of the agencies reported raising their prices in 2022. The most frequent hourly rate in 2021 fell within the $150-174/hr range. However, by the start of 2022, the rate had shifted to the $175-199/hr range. The average rates climbed even higher by the beginning of 2023, primarily driven by Studio agencies catching up a bit, half of which raised their prices last year, compared to only 28% in 2021.
How Digital Agencies Are Structured
Various revgen functions will be performed by a partner, employee, or outside vendor (outsourced). This evolves and changes as digital agencies grow. In the following pages, we are demonstrating who typically handles each function for each agency size.
Studio (0-9 FTEs)
Revgen at Studio shops is driven almost solely by the owners or partners. It’s rare to have dedicated sales or marketing team members in agencies this size. They are simply unable to support that level of additional overhead. This is why it’s critical for founding agency teams to have a partner who is well-suited for sales.
Small (10-24 FTEs)
In Small shops, owners or partners are still responsible for the bulk of the revenue generation, but as shops grow to the larger end of this range, we start seeing VPs of marketing and sales appear. The VP of marketing may begin to have some direct reports here, but most of the time, they’re managing vendors for specific marketing initiatives (content creation, PPC management, design, etc.). It’s also rare for the VP of Sales to have any direct reports, but we have seen some cases where there will be an entry-level BDR or SDR on the team.
Medium (25-49 FTEs)
As agencies grow through this stage, they’ll begin to build out their RevGen team. On the marketing side, they’ll start to bring some key activities in-house, giving the VP of Marketing a few direct reports while she still manages contractors to fill in any gaps. We also start to see CMOs pop up here. For sales, the buildout comes in the form of a few BDR/SDRs and Account Managers. We also begin to see true business development roles emerge at this stage as shops seek out partner opportunities.
Large (50+ FTEs)
By now, shops have their base RevGen process figured out so at this stage they’re focused on increasing RevGen capacity and optimizing their processes. What this means for additional headcount depends on an agency’s overall growth strategy. Most of the time it’s adding additional support for the various areas already covered. Sometimes we’ll see Account Executives added who will own a specific vertical.
Key Roles at Digital Agencies [Available in the full report]
Now that we have covered the typical structure of an agency’s revgen system, we will explore the key roles that perform each of the core revgen functions.
Each section will contain a brief description of the activities the roles perform and a list of the key roles and compensation ranges associated with the function. The key roles and compensation data are from our salary surveys covering almost 2,000 individual agency salaries…
When Agencies Hire for Each Function
[Available in the full report]
Now that we have covered the typical structure of an agency’s revgen system, we will explore the key roles that perform each of the core revgen functions.
Each section will contain a brief description of the activities the roles perform and a list of the key roles and compensation ranges associated with the function. The key roles and compensation data are from our salary surveys covering almost 2,000 individual agency salaries…
Referrals Drive Most New Business at Digital Agencies
In a typical digital shop, whether it’s dev, marketing, or design, they will derive most of their leads and revenue through recommendations from other agencies, prior clients, and partners. AKA referrals.
Referrals can be a great way to grow. A robust referral strategy can deliver pre-trusted leads, lower customer acquisition costs, relationship building, network effects, and shorter sales cycles, among other benefits.
Unfortunately, it’s too easy for agency leaders to get lazy about them and neglect proper relationship building along with other aspects of a more complete revgen strategy.
Relying on referrals for the majority of a firm’s revenue generation presents a few challenges.
- The first is their lack of predictability.
- Second, they typically come from people with similar networks, which limits the ability to grow project scopes with new referrals.
- Finally, there’s little to no control over the quality of the referral. When someone sends a referral your way, they’re helping their network. If you don’t help that referral, it can reflect poorly on the referrer and make them less likely to refer new business. This can jeopardize both of the relationships – yours and the referrer and the referrer and their referral.
With that said, a well-planned referral strategy can definitely be a part of a successful revgen strategy as long as it’s in moderation.
How Much Digital Agencies Spend on Sales & Marketing
The average digital agency invests 7.1% of its revenue in sales and marketing activities. This includes everything from salaries to media spend. Unfortunately, this isn’t sufficient to meet the lofty growth goals set at annual strategy meetings. This has historically resulted in an average revenue growth rate of 13% since 2015. In order to grow faster, agencies can either increase their spend here or increase the effectiveness of their current spend.
%
The percent of revenue the average digital agency spends on sales and marketing activities.
What Pricing Methods Digital Agencies Use
Fixed Fee / Project
A common way to price services is with a fixed fee structure. This model is employed by estimating the cost of a project and then adding a margin to arrive at a fixed fee the client will pay. This type of model includes retainer-based billing along with progress-based billing.
This model works best with clients who have a set budget they’re unable to exceed and need to know project costs beforehand. Both parties assume risk with these types of arrangements, as both cost overruns and savings are absorbed by the agencies. Fixed-fee models also may limit agency revenue growth as the option to add additional services typically isn’t available until the contract renewal time.
Hourly / Time & Materials
This is the simplest pricing model and is often employed by firms in their early stages. Here agencies price their services based on the costs and time required to perform those services and then bill on a periodic basis based on the time incurred. There can be a blended “firm-wide” hourly rate charged or different rates based on the skill level of the individuals working on the project.
Value-based
Pricing services based on the value an agency’s work generates for a client is the goal for most agencies as it aligns the agency’s and client’s goals more than the fixed-fee model and can generate substantial profits for the agency. Agencies typically experience pushback when selling this model, as value-based prices can be much higher than cost-plus pricing. This model is best employed by experienced, proven agencies that can point to successes to help clients understand the return on investment.
Performance-based
This is where agencies (typically marketing agencies vs. dev or design) will charge a fee based on the change in a particular performance metric that they influence. This metric is often sales, but it could also be something more targeted that the client’s measuring like page views, social engagement, leads generated, etc.
The Most Popular Pricing Methods at Digital Agencies
It’s incredibly common for agencies to employ multiple pricing strategies at a time. In our State of Digital Services report, respondents reported an average of 2.6 different methods. Seventy-five percent of firms used Time & Materials and Retainer models, while 65% used Fixed Bid pricing, and only 37% used Value-based pricing.
Agencies utilizing Time & Materials, Fixed Bid, and Retainer pricing models exhibited slightly below-average growth rates and profitability. However, those using Value-based pricing saw a slightly higher-than-average growth rate of 19% year-over-year, and they were more profitable, with an average net income of 18% in 2022. Performance-based pricing, used by only 5% of agencies, led to notably faster growth at 22% and higher profitability with average margins of 17%.
Since 2018, the average growth rate for agencies using Value-based pricing has fluctuated considerably. This pricing strategy tends to correspond with faster-than-average growth during market upswings, but it tends to underperform during turbulent times. Agencies using Time & Materials and Retainer pricing models generally exhibit more stable growth rates.
Revgen Strategies in Detail
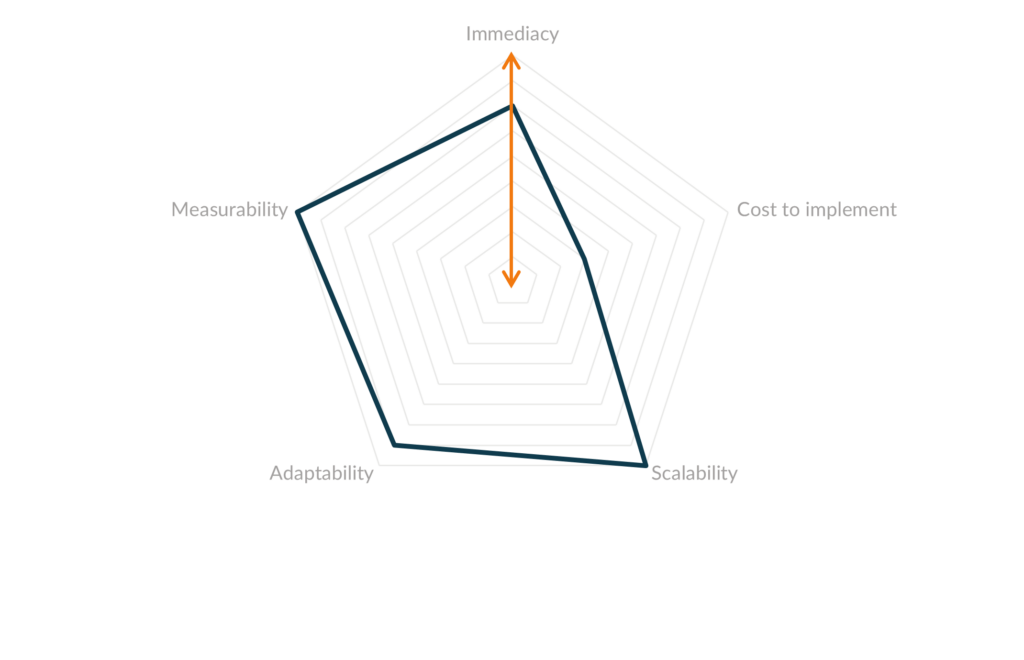
Successful agencies will employ a few main revgen strategies and focus the vast majority of their efforts on becoming experts in them. Agencies who struggle with revgen typically jump from one strategy to the next without ever building enough competency to have consistent success. Therefore, we typically advise clients to select a few options that match their agency’s current needs. We can evaluate the various strategies across five key components:
Immediacy – How quickly will the average agency see results?
Cost to implement – How relatively expensive is the strategy to implement?
Scalability – How well does the strategy scale as the company grows?
Adaptability – How easy is it to change course with shifts in the overall marketplace?
Measurability – How easy is it to understand the ROI?
Evaluating Various Strategies
Here, we evaluate and compare the various strategies across these five core components. The closer the strategy’s line is to the center for a specific component, the worse it is in that area. The goal of these visualizations is to provide a rough idea of how the strategies relate to one another.
A full evaluation of the following revenue generation strategies is available in the full report:
- Cold Outreach
- Cross-selling
- Upselling
- Paid Ads
- Inbound Marketing & SEO
- Procurement & RFPs
- Partnerships
- Events, Conferences & Conventions
- Referrals
Digital Agency Revgen is Broken
Agency revgen is broken. Most digital agencies underinvest in their revgen systems in terms of dollars, effort, and strategy. This causes inconsistent revenue generation, poor alignment, adversarial relationships, and ultimately, a continually undifferentiated value proposition.
Feast or Famine
Inconsistent revenue generation is often due to the overreliance on owners/partners for lead generation and sales. When there’s a lack of leads, they’re compelled to shift their focus to sales. Their heroic efforts tend to work. The issue arises when they shift their focus away from lead gen and sales. This can happen because they need to help service new clients, general business ops needs, or the allure of other shiny objects.
The result is a roller coaster of lead gen and sales that causes significant strain on the agency. This makes accurately forecasting revenue, and thus capacity needs, nearly impossible. We tend to see issues with utilization rates (both too high and too low depending on where they are in the cycle) that manifest in abysmal profit margins, difficulty retaining staff and clients, or both.
Secondly, an overreliance on referrals can also backfire. While referral growth can be robust during great economic environments, recessions can bring them to a halt almost instantly. This leaves agencies scrambling to find new leads and relying, once again, on the heroic efforts of owners and partners. Poor utilization rates, reduced profit margins, and plummeting morale are some of the downstream problems that arise from this inconsistent revenue.
Poor Alignment & Adversarial Relationships
Too many digital agencies have revgen functions that are misaligned or even adversarial at times. Even the simplest issue of a disconnect between the marketing messages and the sales copy confuses prospects and makes sales more complicated than necessary.
When things get choppy, employees default to blaming other departments for poor lead quality, lack of effort, or poor research. This misalignment negatively impacts overall revenue generation and causes additional managerial challenges that sap focus. The bulk of these issues stem from a lack of knowledge about what each function is responsible for and how to actually help one another.
Undifferentiated Value Propositions
At our last count, there were over 45,000 digital agencies operating in the United States. In our survey work, we’ve found that right around half of digital shops consider themselves specialists. That’s an immense amount of noise for a company to sift through to find an agency to solve its problems.
This is where the agency’s strategy has a direct impact on its ability to generate revenue. Many digital agencies go to market with undifferentiated value propositions that don’t resonate with clients. Their customer acquisition cost is higher due to lower conversion rates near the top half of the buyer funnels. This also exacerbates alignment issues.
While this seems like a top-down issue, the differentiated value proposition that will resonate with your target buyer should be uncovered by your front-line salespeople. A proper system would then translate that through marketing, bizdev, account management, and up through leadership. This is not how most revgen systems at digital agencies operate today.
New Strategy & Structure
If we’re to fix what’s broken, our system must address the feast or famine, alignment, and differentiation issues head-on. While agencies can solve some of these with a traditional revgen structure buildout, it falls short of fully fixing all of them. We’ve seen numerous agencies with these functions fully built out that still have issues with strategic alignment and differentiated value propositions. To truly repair revgen, we’re proposing the following steps:

Download the Full Report
The full report contains everything you’ve read here, plus a full process for restructuring revgen at digital agencies, a full section on implementation dynamics, and a final section on the outlook for digital agencies.
Our latest insights on running digital agencies
Exclusive research opportunities, thoughts, and advice on the digital agency industry every two weeks.

"Best / most valuable updates from anyone in ages. I get hit up soooooo much, keep this kind of newsletter / value up."
Wil Reynolds
CEO, Seer Interactive



